Library Management System Testing Report
Submission for the practical exam of Software Quality Assurance course (SEN 305) at Suez Canal University
1 Project Overview
This document serves as the testing report performed by the authors as part of the Software Quality Assurance course (SEN 305) for the year 2025/2026 at Suez Canal University.
This report first presents the project chosen by us to be tested along with our justification for selecting this project. Then, it details the requirements and features expected from the project. After that, the report describes the testing stages we performed, the details of each stage, and the results obtained from them. It concludes with a summary of finding and a table of bugs discovered during the testing process.
The code for our final project can be found in this GitHub repository.
1.1 Project Selection
According to the practical exam guidelines, we were required to select a software system to test. To keep the task focused on testing rather than development, students are allowed to use an existing open-source project from GitHub.
The guidlines also specified that the project must offer:
- Login/Registration functionality.
- CRUD operations (Create, Read, Update, Delete).
Since the course discussed testing tools using Python, we decided to select a project where the backend is implemented using Python.
We also prefered to test a web-based application rather than a desktop or mobile application due to the popularity of testing tools and frameworks for web applications. Moreover, we had more experience working with web applications in our previous courses.
We also wanted a project to be built using modern tools and technologies. In particular, we wanted the project to be set up using docker to ensure consistent environment across all the team members.
After carefully researching open-source projects on GitHub that met the above criteria, we decided to initialize the project with the full-stack-fastapi-template repository by the FastAPI team. This is a popular and well-maintained repository with over 39k stars on GitHub, 75 contributors, and frequent updates (over 1,100 commits).
1.2 Project Description
Upon initializing the repo, this is a generic inventory management system. It provides
- User authentication (login, registration, password reset)
- User profile management
- CRUD operations for items
- Admin dashboard for managing users and items
- REST API for all functionalities
We decided to manipulate the project to turn it into a Library Management System. We added two entities: Books and Journals. Each entity has its own set of attributes and all CRUD operations are supported for both entities. The frontend was also updated to include pages for managing books and journals.
The final project used the following technologies:
- PostgreSQL as the database
- Python + FastAPI for the backend
- React + Vite for the frontend
- Docker for containerization
- Swagger for API documentation
2 Requirements and Features
To facilitate the testing process, we created a table listing the main features expected from the system.
| Feature ID | Feature Description |
|---|---|
| F01 | User Registration |
| F02 | User Login |
| F03 | User Profile Management |
| F04 | Add New Book |
| F05 | View Book Details |
| F06 | Update Book Information |
| F07 | Delete Book |
| F08 | Add New Journal |
| F09 | View Journal Details |
| F10 | Update Journal Information |
| F11 | Delete Journal |
| F12 | Admin Dashboard Access |
| F13 | Add New User by Admin |
| F14 | View User List by Admin |
| F15 | Update User Information by Admin |
| F16 | Delete User by Admin |
These features are written in a clear and concise manner to ensure that they can be easily understood and tested. At this stage, the description of each feature is kept high-level without going into details. However, during the testing process, the test cases will provide more specific details about the expected behavior of each feature.
3 Exploratory Testing Results
In exploratory testing, the goal is for testers to try and explore the system without predefined test cases. Here testers rely on their intuition and previous experience to find bugs in the system.
3.1 Our Strategy
In the exploratory testing phase, we tried to test all the main features in the system as listed in Table 1. In other words, we tried to cover every possible use case for the system.
We also tried to to use our intuition and previous experience with web application to find possible edge cases and scenarios that might lead to bugs.
After performing exploratory testing, we documented the issues we found along with steps to reproduce them and their severity levels.
3.2 Exploratory Testing Findings
During our exploratory testing, we identified a bug in related to the system’s usability. We will now describe the bug in detail and Section 7 will mention it again along with other bugs found during other testing stages.
After logging in and moving to the dashboard, the system performs correctly and shows “Hi [user name]” message. If the user opened the inspector tool (F12) and opened the Application tab, he will see that the local storage contains a key named “access_token” with the value being the JWT token created by the backend during login to validate the user’s session.
If the user alters the value of this key and refreshes the page, the system does not redirect the user to the login page. Instead, the dashboard loads with the message “Hi [empty space]”. This indicates that the system loads the dashboard prior to validating the token stored in local storage. Only after the dashboard loads with some time, the system invalidates the token and redirects the user to the login page.
4 Manual Testing Stage
In the manual testing stage, we create a much more detailed description of the test cases to be performed on the system. Then, we manually execute each of these tests and record our findings.
4.1 Manual Testing Cases
The table below lists the test cases we created for the manual testing stage. To enhance the table’s readability, we divided the table into two parts. The first part covers features related to login/regestration, user portfolio management, and books management. The second part covers journals management and admin functionalities.
| Test Case ID | Feature ID | Test Case Description | Expected Result |
|---|---|---|---|
| TC01 | F01 | Register a new user with valid details | User is registered successfully and redirected to login page |
| TC02 | F01 | Register a new user with an existing email | Error message “Email already exists” is displayed |
| TC03 | F01 | Register a user with invalid email format | Error message “Invalid email format” is displayed |
| TC04 | F01 | Register a user with 3 characters password | Error message “Password too short” is displayed |
| TC05 | F02 | Login with valid credentials | User is logged in and redirected to dashboard |
| TC06 | F02 | Login with correct email and wrong password | Error message is displayed |
| TC07 | F02 | Login with unregistered email | Error message is displayed |
| TC08 | F03 | Update user name and save changes | User profile is updated successfully |
| TC09 | F03 | Update user email to an existing email | Error message “Email already exists” is displayed |
| TC10 | F03 | Update user password with less than 6 characters | Error message “Password too short” is displayed |
| TC11 | F04 | Add a new book with valid details | Book is added successfully and appears in the book list |
| TC12 | F04 | Add a new book with missing required fields | Error message “Please fill all required fields” is displayed |
| TC13 | F04 | Add a new book with invalid ISBN format | Error message “Invalid ISBN format” is displayed |
| TC14 | F05 | View list of books | List of books is displayed correctly containing only books added by the user (except admin) |
| TC15 | F06 | Update book information with valid details | Book information is updated successfully |
| TC16 | F06 | Update book information with missing required fields | Error message “Please fill all required fields” is displayed |
| TC17 | F06 | Update book information with invalid ISBN format | Error message “Invalid ISBN format” is displayed |
| TC18 | F07 | Delete a book | Book is deleted successfully and removed from the book list |
| Test Case ID | Feature ID | Test Case Description | Expected Result |
|---|---|---|---|
| TC19 | F08 | Add a new journal with valid details | Journal is added successfully and appears in the journal list |
| TC20 | F08 | Add a new journal with missing required fields | Error message “Please fill all required fields” is displayed |
| TC21 | F08 | Add a new journal with invalid ISSN format | Error message “Invalid ISSN format” is displayed |
| TC22 | F09 | View list of journals | List of journals is displayed correctly containing only journals added by the user (except admin) |
| TC23 | F10 | Update journal information with valid details | Journal information is updated successfully |
| TC24 | F10 | Update journal information with missing required fields | Error message “Please fill all required fields” is displayed |
| TC25 | F10 | Update journal information with invalid ISSN format | Error message “Invalid ISSN format” is displayed |
| TC26 | F11 | Delete a journal | Journal is deleted successfully and removed from the journal list |
| TC27 | F12 | Access admin dashboard with admin account | Admin dashboard is displayed correctly with user management options |
| TC28 | F12 | Access dashboard with non-admin account | No user management options are displayed |
| TC29 | F13 | Add a new user by admin with valid details | User is added successfully and appears in the user list |
| TC30 | F14 | View user list by admin | List of users is displayed correctly |
| TC31 | F15 | Update user information by admin with valid details | User information is updated successfully |
| TC32 | F16 | Delete a user by admin | User is deleted successfully and removed from the user list |
We created these test cases to cover all the main features of the system. Each test case includes a unique ID, the feature it tests, a description of the test case, and the expected result.
4.2 Manual Testing Results
After specifying the test cases, we manually executed each test case and recorded the actual results. The following table shows the actual result for each test case and whether it passed or failed.
| Test Case ID | Actual Result | Status |
|---|---|---|
| TC01 | User registered successfully and redirected to login page | Passed |
| TC02 | Error message “The user with this email already exists in the system” | Passed |
| TC03 | Error message “Invalid email address” | Passed |
| TC04 | Error message “Password must be at least 8 characters” | Passed |
| TC05 | User logged in and redirected to dashboard | Passed |
| TC06 | Error message “Incorrect email or password” | Passed |
| TC07 | Error message “Incorrect email or password” | Passed |
| TC08 | User profile updated successfully | Passed |
| TC09 | Error message “User with this email already exists” | Passed |
| TC10 | Error message “Password must be at least 8 characters” | Passed |
| TC11 | Book added successfully and appears in the book list | Passed |
| TC12 | Save button is disabled until all required fields are filled | Passed |
| TC13 | The system accepted the invalid ISBN format (bug found) | Failed |
| TC14 | List of books displayed correctly | Passed |
| TC15 | Book information updated successfully | Passed |
| TC16 | Empty required fields are highlighted with error messages | Passed |
| TC17 | The system accepted the invalid ISBN format (bug found) | Failed |
| TC18 | Book deleted successfully and removed from the book list | Passed |
| Test Case ID | Actual Result | Status |
|---|---|---|
| TC19 | Journal added successfully and appears in the journal list | Passed |
| TC20 | Save button is disabled until all required fields are filled | Passed |
| TC21 | The system accepted the invalid ISSN format (bug found) | Failed |
| TC22 | List of journals displayed correctly | Passed |
| TC23 | Journal information updated successfully | Passed |
| TC24 | Empty required fields are highlighted with error messages | Passed |
| TC25 | The system accepted the invalid ISSN format (bug found) | Failed |
| TC26 | Journal deleted successfully and removed from the journal list | Passed |
| TC27 | Admin dashboard displayed correctly with user management options | Passed |
| TC28 | No user management options are displayed | Passed |
| TC29 | User added successfully and appears in the user list | Passed |
| TC30 | List of all users displayed correctly | Passed |
| TC31 | User information updated successfully | Passed |
| TC32 | User deleted successfully and removed from the user list | Passed |
Out of the 32 test cases, 28 passed successfully while 4 failed due to bugs related to input validation for ISBN and ISSN formats.
5 White Box Testing
White box testing involves testing the internal logic and structure of the code. In this stage, we created automated test cases to test specific functions and methods in the codebase.
The backend of the system is built using FastAPI, which is a Python web framework. We used pytest as the testing framework to create and run our automated tests. Some of these tests used internal knowledge of the codebase (white box testing) while others focused on testing the API endpoints (black box testing).
The repo we used had some initial test cases. We expanded on these test cases to cover the new features we added to the system (Books and Journals management).
Three testing scripts were used for white box testing:
backend/app/tests/crud/test_book.py: Contains unit tests for the CRUD operations related to Books.backend/app/tests/crud/test_journal.py: Contains unit tests for the CRUD operations related to Journals.backend/app/tests/crud/test_user.py: Contains unit tests for the CRUD operations related to Users.
In this report, we are going to focus on the 5 test cases defined in test_book.py as examples of the white box testing we performed.
Since pytest manages both the white box and black box testing stages, we are going to discuss the test results and code coverage in Section 6.
5.1 Books CRUD Operations Tests
The test_book.py script contains the following test cases for the Books CRUD operations:
test_create_booktest_get_book_by_idtest_get_bookstest_update_booktest_delete_book
We are going to show the code for these test cases and briefly explain each one.
5.1.1 test_create_book
def test_create_book(db: Session) -> None:
user = create_random_user(db)
book_create = BookCreate(
title="Test Book",
author="Test Author",
isbn="1234567890",
description="Test Description",
)
book = crud.create_book(
session=db, book_in=book_create, owner_id=user.id
)
assert book.title == book_create.title
assert book.author == book_create.author
assert book.isbn == book_create.isbn
assert book.description == book_create.description
assert book.owner_id == user.idThis test case verifies that a new book can be created successfully. It creates a random user, then creates a book with specific details, and finally asserts that the created book’s attributes match the input values.
The create_random_user function is a helper function that creates a user with random details for testing purposes. It is defined in backend/app/tests/utils/user.py.
The db parameter is provided by a pytest fixture that sets up a test database session. It can be found in backend/app/tests/conftest.py.
5.1.2 test_get_book_by_id
def test_get_book_by_id(db: Session) -> None:
book = create_random_book(db)
found = crud.get_book_by_id(session=db, id=book.id)
assert found
assert found.id == book.id
assert found.title == book.titleThis test case verifies that a book can be retrieved by its ID. It creates a random book, then retrieves it using its ID, and asserts that the retrieved book’s attributes match the original book’s attributes.
5.1.3 test_get_books
def test_get_books(db: Session) -> None:
book1 = create_random_book(db)
book2 = create_random_book(db)
books = crud.get_books(session=db, owner_id=None)
ids = [b.id for b in books]
assert book1.id in ids
assert book2.id in idsThis test case verifies that multiple books can be retrieved. It creates two random books, then retrieves all books, and asserts that the created books are present in the retrieved list by checking their IDs.
5.1.4 test_update_book
def test_update_book(db: Session) -> None:
book = create_random_book(db)
update_in = BookUpdate(title="Updated Title")
updated = crud.update_book(session=db, db_book=book, book_in=update_in)
assert updated.title == "Updated Title"
assert updated.id == book.idThis test case verifies that a book’s information can be updated. It creates a random book, then updates its title, and asserts that the updated book’s title matches the new value while its ID remains unchanged.
5.1.5 test_delete_book
def test_delete_book(db: Session) -> None:
book = create_random_book(db)
crud.delete_book(session=db, db_book=book)
found = crud.get_book_by_id(session=db, id=book.id)
assert found is NoneThis test case verifies that a book can be deleted. It creates a random book, deletes it, and then attempts to retrieve it by its ID, asserting that the book is no longer found.
6 Black Box Testing
In the black box testing stage, we focused on testing the API endpoints of the system without any knowledge of the internal code structure. We created automated test cases to test the various API endpoints for Books and Journals management. These API endpoints can be quickly explored from the Swagger documentation.
The black box tests were defined in the folder backend/app/tests/api/routes. The following testing scripts were used for black box testing:
test_books.py: Contains API tests for Books management endpoints.test_items.py: Contains API tests for Items management endpoints.test_journals.py: Contains API tests for Journals management endpoints.test_login.py: Contains API tests for authentication endpoints.test_private.py: Contains API tests for user creation endpoints.test_users.py: Contains API tests for Users management endpoints.
In this report, we will cover the 11 test cases defined in test_books.py as examples of the black box testing we performed.
6.1 Books API Endpoints Tests
The test_books.py script contains the following test cases for the Books API endpoints:
test_create_booktest_read_booktest_read_book_not_foundtest_read_book_not_enough_permissionstest_read_bookstest_update_booktest_update_book_not_foundtest_update_book_not_enough_permissionstest_delete_booktest_delete_book_not_foundtest_delete_book_not_enough_permissions
We are going to show the code for these test cases and briefly explain each one.
6.1.1 test_create_book
def test_create_book(
client: TestClient, superuser_token_headers: dict[str, str]
) -> None:
data = {
"title": "FooBook",
"author": "AuthorName",
"isbn": "1234567890",
"description": "A book description."
}
response = client.post(
f"{settings.API_V1_STR}/books/",
headers=superuser_token_headers,
json=data,
)
assert response.status_code == 200
content = response.json()
assert content["title"] == data["title"]
assert content["author"] == data["author"]
assert content["isbn"] == data["isbn"]
assert content["description"] == data["description"]
assert "id" in content
assert "owner_id" in contentThis test case checks the API endpoint for creating a new book. It sends a POST request with book details and asserts that the response status code is 200 (OK) and that the returned book details match the input data.
The client parameter is a pytest fixture that provides a test client for making API requests. The superuser_token_headers parameter is another fixture that provides authentication headers for a superuser (admin). These fixtures can be found in backend/app/tests/conftest.py.
6.1.2 test_read_book
def test_read_book(
client: TestClient, superuser_token_headers: dict[str, str], db: Session
) -> None:
book = create_random_book(db)
response = client.get(
f"{settings.API_V1_STR}/books/{book.id}",
headers=superuser_token_headers,
)
assert response.status_code == 200
content = response.json()
assert content["title"] == book.title
assert content["author"] == book.author
assert content["isbn"] == book.isbn
assert content["description"] == book.description
assert content["id"] == str(book.id)
assert content["owner_id"] == str(book.owner_id)This test case checks the API endpoint for retrieving a book by its ID. It creates a random book, saves it in the database, sends a GET request to retrieve it, and asserts that the response status code is 200 (OK) and that the returned book details match the original book’s attributes.
6.1.3 test_read_book_not_found
def test_read_book_not_found(
client: TestClient, superuser_token_headers: dict[str, str]
) -> None:
response = client.get(
f"{settings.API_V1_STR}/books/{uuid.uuid4()}",
headers=superuser_token_headers,
)
assert response.status_code == 404
content = response.json()
assert content["detail"] == "Book not found"This test case checks the API endpoint for retrieving a book that does not exist. It sends a GET request with a random UUID (to ensure it does not exist) and asserts that the response status code is 404 (Not Found) and that the error message indicates that the book was not found.
6.1.4 test_read_book_not_enough_permissions
def test_read_book_not_enough_permissions(
client: TestClient, normal_user_token_headers: dict[str, str], db: Session
) -> None:
book = create_random_book(db)
response = client.get(
f"{settings.API_V1_STR}/books/{book.id}",
headers=normal_user_token_headers,
)
assert response.status_code == 400
content = response.json()
assert content["detail"] == "Not enough permissions"This test case checks the API endpoint for retrieving a book when the user does not have enough permissions. It creates a random book, sends a GET request using a normal user’s authentication headers, and asserts that the response status code is 400 (Bad Request). This is because only the owner or admin can view the book details.
6.1.5 test_read_books
def test_read_books(
client: TestClient, superuser_token_headers: dict[str, str], db: Session
) -> None:
create_random_book(db)
create_random_book(db)
response = client.get(
f"{settings.API_V1_STR}/books/",
headers=superuser_token_headers,
)
assert response.status_code == 200
content = response.json()
assert len(content["data"]) >= 2This test case checks the API endpoint for retrieving multiple books. It creates two random books, sends a GET request to retrieve all books, and asserts that the response status code is 200 (OK) and that at least two books are returned in the response data.
6.1.6 test_update_book
def test_update_book(
client: TestClient, superuser_token_headers: dict[str, str], db: Session
) -> None:
book = create_random_book(db)
data = {
"title": "Updated Book Title",
"author": book.author,
"isbn": book.isbn,
"description": book.description
}
response = client.put(
f"{settings.API_V1_STR}/books/{book.id}",
headers=superuser_token_headers,
json=data,
)
assert response.status_code == 200
content = response.json()
assert content["title"] == data["title"]
assert content["id"] == str(book.id)
assert content["owner_id"] == str(book.owner_id)This test case checks the API endpoint for updating a book’s information. It creates a random book, sends a PUT request with updated title, and asserts that the response status code is 200 (OK) and that the returned book details reflect the updates.
6.1.7 test_update_book_not_found
def test_update_book_not_found(
client: TestClient, superuser_token_headers: dict[str, str]
) -> None:
data = {
"title": "Updated Book Title",
"author": "AuthorName",
"isbn": "1234567890",
"description": "A book description."
}
response = client.put(
f"{settings.API_V1_STR}/books/{uuid.uuid4()}",
headers=superuser_token_headers,
json=data,
)
assert response.status_code == 404
content = response.json()
assert content["detail"] == "Book not found"This test case checks the API endpoint for updating a book that does not exist. It sends a PUT request with a random UUID (to ensure it does not exist) and asserts that the response status code is 404 (Not Found) and that the error message indicates that the book was not found.
6.1.8 test_update_book_not_enough_permissions
def test_update_book_not_enough_permissions(
client: TestClient, normal_user_token_headers: dict[str, str], db: Session
) -> None:
book = create_random_book(db)
data = {
"title": "Updated Book Title",
"author": book.author,
"isbn": book.isbn,
"description": book.description
}
response = client.put(
f"{settings.API_V1_STR}/books/{book.id}",
headers=normal_user_token_headers,
json=data,
)
assert response.status_code == 400
content = response.json()
assert content["detail"] == "Not enough permissions"This test case checks the API endpoint for updating a book’s information when the user does not have enough permissions. It creates a random book, sends a PUT request with updated title using a normal user’s authentication headers, and asserts that the response status code is 400 (Bad Request) and that the error message shows insufficient permissions.
6.1.9 test_delete_book
def test_delete_book(
client: TestClient, superuser_token_headers: dict[str, str], db: Session
) -> None:
book = create_random_book(db)
response = client.delete(
f"{settings.API_V1_STR}/books/{book.id}",
headers=superuser_token_headers,
)
assert response.status_code == 200
content = response.json()
assert content["message"] == "Book deleted successfully"This test case checks the API endpoint for deleting a book. It creates a random book, sends a DELETE request, and asserts that the response status code is 200 (OK) and that the success message indicates the book was deleted successfully. Note that the user here is a superuser (admin).
6.1.10 test_delete_book_not_found
def test_delete_book_not_found(
client: TestClient, superuser_token_headers: dict[str, str]
) -> None:
response = client.delete(
f"{settings.API_V1_STR}/books/{uuid.uuid4()}",
headers=superuser_token_headers,
)
assert response.status_code == 404
content = response.json()
assert content["detail"] == "Book not found"This test case checks the API endpoint for deleting a book that does not exist. It sends a DELETE request with a random UUID (to ensure it does not exist) and asserts that the response status code is 404 (Not Found) and that the error message indicates that the book was not found.
6.1.11 test_delete_book_not_enough_permissions
def test_delete_book_not_enough_permissions(
client: TestClient, normal_user_token_headers: dict[str, str], db: Session
) -> None:
book = create_random_book(db)
response = client.delete(
f"{settings.API_V1_STR}/books/{book.id}",
headers=normal_user_token_headers,
)
assert response.status_code == 400
content = response.json()
assert content["detail"] == "Not enough permissions"This test case checks the API endpoint for deleting a book when the user does not have enough permissions. It creates a random book, sends a DELETE request using a normal user’s authentication headers, and asserts that the response status code is 400 (Bad Request) and that the error message shows insufficient permissions.
6.2 Automated Tests Results
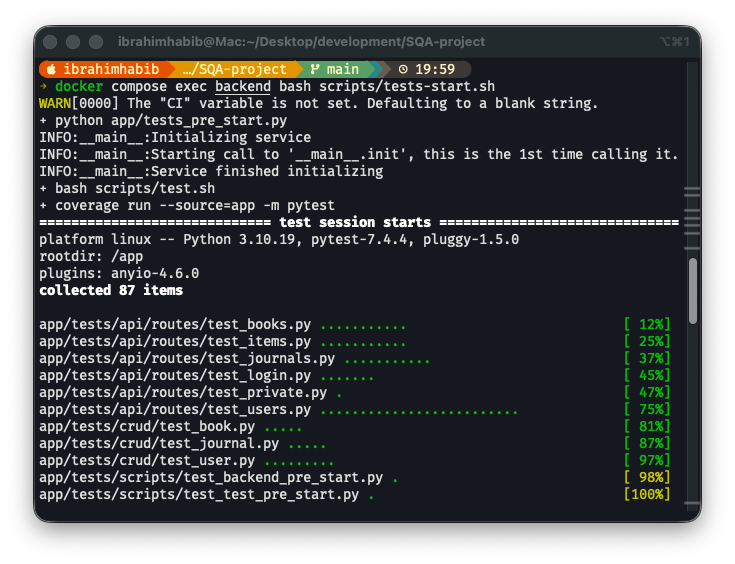
After defining the automated test cases for both white box and black box testing stages, we executed all the tests using pytest. The following table image shows the test results.
In Figure 4, we can see that all the automated tests passed successfully. Each green dot represents a passed test case. Since all tests are green, there are no failed tests.
6.3 Code Coverage
One of the advantages of using pytest is its ability to automatically measure code coverage. Code coverage indicates the percentage of the codebase that is executed during testing. Higher code coverage generally implies better test coverage and a lower likelihood of undetected bugs.
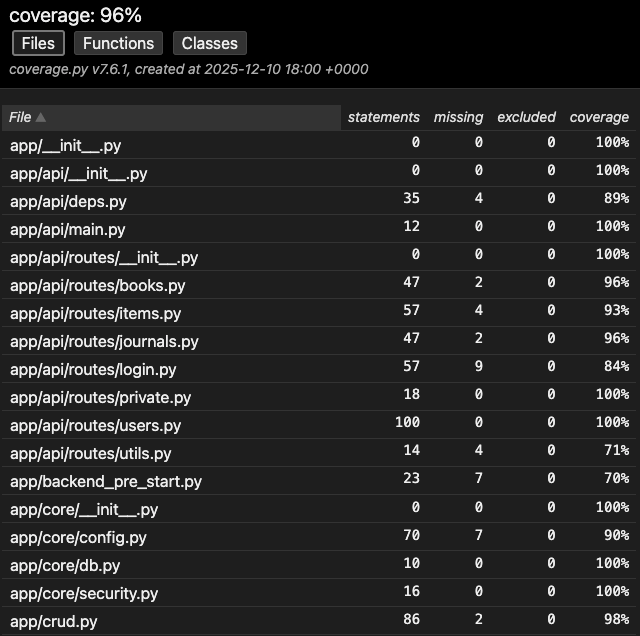
pytest generates an HTML report for code coverage that can be viewed in a web browser. The following image shows a snippet of the code coverage report.
The overall code coverage achieved during our testing process is 96%, as shown in Figure 5 in the top of the page. For each file, the report shows the number of statements covered by tests, the number uncovered ,and the percentage of coverage. Most files have 100% coverage, while a few files have slightly lower coverage. Some of these files are related to db setup and configuration, which are not directly tested.
7 Bug Reports
Before we conclude this report, we will summarize the bugs we found during the different testing stages.
The table below lists the bugs we found along with their severity levels, reproduction steps, the expected behavior, and the actual behavior. To enhance the table’s readability, we have broken down the table into multiple parts with different columns shown in each part. The bug IDs are consistent across all parts.
| Bug ID | Severity Level | Description |
|---|---|---|
| B01 | Medium | Input validation bug for ISBN format when adding a new book. The system accepts invalid ISBN formats. |
| B02 | Medium | Input validation bug for ISBN format when updating book information. The system accepts invalid ISBN formats. |
| B03 | Medium | Input validation bug for ISSN format when adding a new journal. The system accepts invalid ISSN formats. |
| B04 | Medium | Input validation bug for ISSN format when updating journal information. The system accepts invalid ISSN formats. |
| B05 | Low | Usability bug related to token validation on dashboard load. The system loads the dashboard before validating the token, leading to a brief display of incorrect user information. |
| Bug ID | Steps to Reproduce |
|---|---|
| B01 | 1. Navigate to the “Add New Book” page. 2. Fill in the book details with an invalid ISBN format. 3. Click the “Save” button. |
| B02 | 1. Navigate to the “Update Book” page for an existing book. 2. Modify the book details with an invalid ISBN format. 3. Click the “Save” button. |
| B03 | 1. Navigate to the “Add New Journal” page. 2. Fill in the journal details with an invalid ISSN format. 3. Click the “Save” button. |
| B04 | 1. Navigate to the “Update Journal” page for an existing journal. 2. Modify the journal details with an invalid ISSN format. 3. Click the “Save” button. |
| B05 | 1. Log in to the system. 2. Open the browser’s inspector tool (F12) and go to the Application tab. 3. Modify the “access_token” value in local storage to an invalid value. |
| Bug ID | Expected Behavior | Actual Behavior |
|---|---|---|
| B01 | The system should display an error message indicating that the ISBN format is invalid and prevent the book from being added. | The system accepts the invalid ISBN format and adds the book successfully. |
| B02 | The system should display an error message indicating that the ISBN format is invalid and prevent the book information from being updated. | The system accepts the invalid ISBN format and updates the book information successfully. |
| B03 | The system should display an error message indicating that the ISSN format is invalid and prevent the journal from being added. | The system accepts the invalid ISSN format and adds the journal successfully. |
| B04 | The system should display an error message indicating that the ISSN format is invalid and prevent the journal information from being updated. | The system accepts the invalid ISSN format and updates the journal information successfully. |
| B05 | The system should validate the token before loading the dashboard and redirect the user to the login page if the token is invalid. | The system loads the dashboard before validating the token, leading to a brief display of incorrect user information before redirecting to the login page. |
8 Conclusion
In this report, we described our process for testing the Library Management System.
The project was initialized from a GitHub repo that provided a basic implementation of user authentication and item management features. We expanded the system by adding Books and Journals management functionalities.
To test the system, we started by listing the major system features. Then, we created manual test cases to cover these features and executed them, recording the results.
We also developed automated test cases for both white box and black box testing stages using pytest. We executed all the automated tests and achieved a high code coverage of 96%.
8.1 Acknowledgments
- Dr. Samah Zakaria: For her Software Quality Assurance course and continuous support.
- Dr. Mirhan Hisham: For her valuable hands-on sessions.